MINIMIZE SECURITY GAPS WITH MULTI-FACTOR AUTHENTICATION
Fraudsters and cyber-criminals are opportunists. COVID-19 has proven that there is no circumstance that hackers will not seek to exploit. They know that the confusion caused by this worldwide pandemic can be used to try to steal sensitive information from individuals and organizations alike. Cyber-attacks already made headlines on an almost daily basis. Now, hackers are tapping into the wealth of insecurely protected data and hiding behind the confusion caused by a global pandemic, while reaping the rewards.
Organizations are aware of these attacks, but many still don’t seem to realize just how dangerous and sophisticated hackers have become. Many organizations are still not taking the necessary steps to protect their critical data.
Some companies continue to rely on simple password security and spend their money on implementing security practices that do not address the latest hacking techniques.
Passwords have been around for a long time
Passwords have been used for centuries as a way to protect people and information. In the early years of technology, they seemed like the best solution for controlling access to systems with sensitive data.
Over the years, passwords and password encryption methods have become more complex, but as they have improved, so have the skills of cyber-criminals. According to the 2020 Data Breach Investigation Report, stolen passwords have accounted for 81 percent of data breaches in the past few years. One of the fundamental problems is that systems can’t know if the provided password has been compromised. Access is granted solely based on matching credentials. This lack of proof of identity is an obvious flaw in relying exclusively on passwords.
Not being able to prove a user’s identity with a password is one concern, but businesses can’t always monitor employees and users to make sure they are utilizing best practices. Most people use the same or similar passwords for almost all accounts. This creates another security issue that organizations have to consider.
What should organizations do to prevent fraudulent activity?
The ability to verify a user’s claimed identity through various authentication factors has become crucial for NonStop systems, especially for users that will be logging-on to business-critical applications. Ineffective authentication comes with significant direct and indirect risks, including compliance penalties, data theft, loss of customer trust, and significant loss of revenue. There is an over-reliance on insecure forms of authentication, such as passwords and security questions, this can lead to security gaps that create opportunities for intruders.
By implementing additional security measures, such as strong passwords and the use of multi-factor authentication, users can prevent credentials from being compromised and avoid falling victim to these types of attacks.
Minimizing Security Gaps With
CSP Authenticator+
Modern authentication methods represent a more robust security structure, and also provide a better user experience when logging into applications. MFA also makes it easier for auditors to get answers to critical compliance questions; providing information such as which users are granted access to which system, and also how the access policy is being reliably enforced. Additionally, some of the modern MFA applications available today also include reporting capabilities, which ensure that compliance standards, such as PCI DSS, are being met.
CSP Authenticator+™ supports numerous authentication factors for NonStop. It provides a RESTful interface that supports multi-factor authenticated logins on NonStop systems. CSP Authenticator+ resides on the NonStop Platform and uses an OSS “bridge” to connect to the RESTful interface of the CSP Authenticator+ web server.
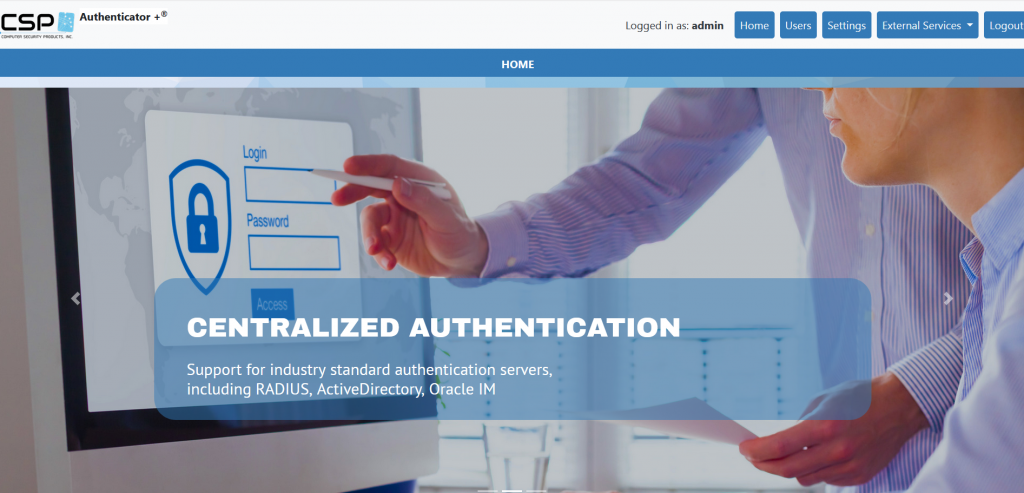
CSP Authenticator+™ Dashboard
CSP Authenticator+ can provide authentication services via Safeguard Authentication SEEP, or Pathway and Non-Pathway servers. Almost any application, including TACL, can now easily support multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Authentication methods such as RADIUS, RSA Cloud, Active Directory, and Open LDAP are supported. Additional authentication methods include RSA SecurID, Email, Text Message, and Google Authenticator. You can now enable MFA logins for different applications, making them more secure!
CSP Authenticator+ Key Features:
- Support for various authentication methods
- Browser-based user-friendly interface
- Standardized authentication across platforms
- Configurable for all or selected users
- Support for virtual addressing
CSP – Compliance at your Fingertips™
For complimentary access to CSP-Wiki®, an extensive repository of NonStop security knowledge and best practices, please visit wiki.cspsecurity.com
We Built the Wiki for NonStop Security ®
+1(905) 568 –8900